I know you’re probably curious about Artificial Intelligence and Types of AI. And why wouldn’t you be? It’s everywhere these days – from our smartphones to our cars, and even our home appliances.
It’s not just a concept from science fiction; it’s a reality that’s transforming our world. AI is about creating systems that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence. But AI isn’t a one-size-fits-all technology.
There are different types, each with its own capabilities and limitations.
In this article, we’ll delve into these types of AI, providing a clear understanding of what they are and their significance in our lives.
So, whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or a curious novice, buckle up for an exciting journey into the diverse world of AI!
Understanding AI
Artificial intelligence is an interesting branch of computer science that seeks to construct machines that replicate human intelligence. It is about developing systems that can think, learn, adapt, and execute activities traditionally associated with human intelligence, including as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. Now let’s look at how Machine Learning comes into the situation.
AI vs Machine Learning
| Feature | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad field of creating intelligent machines | Subfield of AI focused on learning from data |
| Goal | Achieve human-like intelligence and capabilities | Solve specific problems by learning from data |
| Methods | Various approaches, including rule-based systems, expert systems, and machine learning | Primarily uses algorithms trained on data |
| Learning | Can learn and adapt, but not always through data analysis | Learns and improves through data analysis |
| Autonomy | Can be autonomous or require human intervention | Requires human involvement for setup, training, and optimization |
| Examples | Self-driving cars, intelligent assistants, robots | Facial recognition, spam filtering, recommendation systems |
Types Of AI
Artificial intelligence can be easily classified based on its capabilities and functionalities:
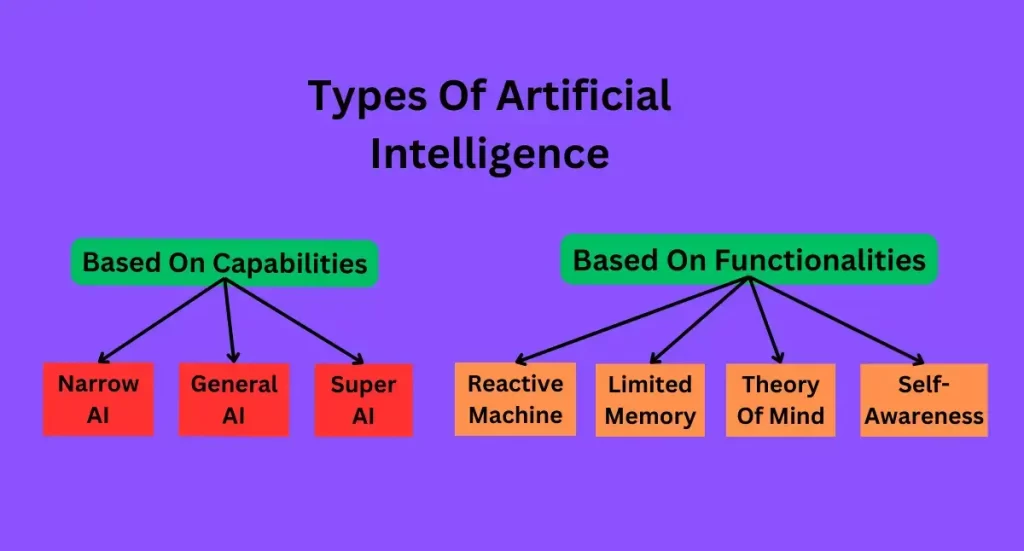
Types of Artificial Intelligence Based on Capabilities
1. Narrow AI
Definition: Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, concentrates on a certain task and cannot perform beyond its constraints. It focuses on a specific subset of cognitive talents and advances within that spectrum. As machine learning and deep learning methodologies advance, narrow AI applications will become more prevalent in our daily lives.
Here are some common examples of narrow AI you encounter daily:
- Virtual assistants: Like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, which understand and respond to your voice commands for specific tasks.
- Spam filters: Automatically identify and block unwanted emails in your inbox.
- Recommendation systems: Suggest products or content you might be interested in based on your past behavior.
- Self-driving cars: Use sensors and algorithms to navigate roads and avoid obstacles.
- Facial recognition software: Identifies individuals in photos and videos.
2. General AI
Definition: General AI, also known as Strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), is a type of AI that can comprehend, absorb, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks at a level comparable to or beyond that of a human. It is not restricted to a single area and can transmit knowledge from one to another.
While true AGI remains elusive, here are some examples of existing AI that might seem like they have general intelligence, but are actually narrow AI performing complex tasks:
- Large language models (like me): We can generate text, translate languages, and answer your questions in an informative way. But we can’t truly understand the world or perform actions in it.
- Self-driving cars: These can navigate roads and avoid obstacles, but they rely on specific algorithms and training data, not general intelligence.
- Chess-playing AI: Advanced systems can beat even the best human players, but they only excel at chess, not other intellectual tasks.
3. Super AI
Definition: Super AI, also known as Superintelligence, refers to hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence in virtually all economically valuable work, including scientific creativity, general wisdom, and social skills. It’s a concept central to discussions about the future impact of AI on society.
Types of Artificial Intelligence Based on Functionalities
1. Reactive Machines
Definition: Reactive Machines can operate in real-time, responding directly to current stimuli without retaining memories. They are incapable of learning or changing.
Examples:
- Deep Blue chess computer: Analyzes the current chessboard state to make the best move but doesn’t learn from past games.
- Traffic light controller: Responds to sensor data (car presence, time of day) to change lights but doesn’t adapt to unexpected traffic patterns.
- Simple reflex-based video game enemies: React to player actions (movement, attacks) but don’t strategize or learn player behavior.
2. Limited Memory Machines
Definition: Limited Memory Machines can store and access past experiences, allowing them to learn and adapt to some extent within their defined tasks.
Examples:
- Self-driving cars: Leverage past traffic data and real-time sensor information to adjust speed and navigate obstacles.
- Spam filters: Analyze email content and user feedback to learn and identify spam more effectively over time.
- Recommendation systems: Track user purchases and browsing behavior to suggest personalized product recommendations.
3. Theory of Mind AI
Definition: The Theory of Mind AI would possess the ability to understand and predict the mental states of others, including emotions, beliefs, and intentions.
Examples:
- Currently not in existence: While advancements in facial expression recognition and sentiment analysis show promise, true “theory of mind” capabilities remain elusive.
- Future scenarios: Imagine AI assistants that anticipate your needs and adjust their responses based on your emotional state or hidden agendas.
4. Self-Aware AI
Definition: Self-Aware AI is more hypothetical type of AI would possess true consciousness and self-awareness, understanding its own existence and place in the world.
Examples:
- Purely science fiction: While concepts like the “Singularity” suggest future possibilities, self-aware AI currently exists only in fiction.
- Philosophical implications: The potential emergence of such AI raises profound questions about consciousness, sentience, and the nature of intelligence.
How Does AI Learn?
AI learns through a variety of techniques and algorithms, depending on the specific task and the type of AI being used. Here are some common approaches to how AI learns:
1. Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, the AI is trained on a labeled dataset, where each input is associated with a corresponding output. The AI learns to map inputs to outputs by minimizing the difference between its predictions and the true labels provided in the training data.
Examples: Neural networks, support vector machines, decision trees, and linear regression
2. Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning involves training the AI on a dataset without explicit labels. The goal is to discover hidden patterns, structures, or relationships within the data. Unsupervised learning frequently involves problems like clustering and dimensionality reduction.
Algorithms such as K-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, principal component analysis (PCA), and autoencoders are used in unsupervised learning.
3. Reinforcement Learning
In reinforcement learning, the AI learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment. The AI receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on its actions. The goal of the AI is to learn a policy that maximizes cumulative rewards over time.
Reinforcement learning algorithms include Q-learning, deep Q-networks (DQN), policy gradients, and actor-critic methods.
4. Deep Learning
Deep learning is a type of machine learning that employs artificial neural networks with numerous layers (hence the name “deep”). Deep learning models are capable of automatically learning hierarchical representations of data, which makes them well-suited for tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are commonly used for image-related tasks, while recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformers are popular for sequential data and natural language processing tasks.
5. Transfer Learning
Transfer learning is the process of applying information from one activity or topic to improve performance on another.
Instead of training a model from scratch, transfer learning allows AI models to transfer knowledge learned from one dataset to another, often with fewer labeled examples required for the target task.
6. Evolutionary Algorithms
Evolutionary algorithms are inspired by biological evolution and natural selection. These algorithms maintain a population of candidate solutions to a problem and iteratively evolve better solutions through processes such as mutation, crossover, and selection.
So, in a nutshell, AI learns by analyzing data, finding patterns, making decisions, and continuously improving through trial and error. Isn’t this fascinating?
Can AI be Autonomous?
Yes, autonomous artificial intelligence (AAI) is an AI system that can function without human assistance. AAI systems can learn from data, make judgments, and carry out tasks without human intervention.
AAI systems differ from typical AI in that they are capable of learning and adapting independently. Traditional AI systems require explicit instructions and ongoing supervision, but AAI systems can understand their surroundings, make judgments, and modify their methods based on the results.
AAI analyzes data, draws conclusions, and completes tasks autonomously using complex algorithms and machine learning models.
Examples of AAI are:
- Innovative manufacturing robots
- Autonomous cars
- Caring robots for seniors
What is The Turing Test?
The Turing Test, named after Alan Turing, is a means to determine if a machine can simulate human behavior. In this test, a human judge communicates with a machine and a human via text.
If the judge is unable to determine which is the machine, it is considered to have passed the test. It is not about the machine producing perfect answers, but about how closely its responses resemble those given by humans.
AI vs AGI
| Feature | AI | AGI |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Narrow intelligence focused on specific tasks. | General intelligence capable of a wide range of tasks like humans. |
| Level of intelligence | Less intelligent than humans. | As intelligent as, or potentially more intelligent than, humans. |
| Learning ability | Requires specific training data and instructions. | Learns independently and adapts to new situations. |
| Scope of tasks | Performs well-defined tasks within a limited domain. | Can understand and perform various tasks across different domains. |
| Development status | Widely available and used in various applications. | Theoretical concept, not yet achieved. |
| Example | Facial recognition software, chess-playing program, recommendation engine. | (Hypothetical) Robot that can write a novel, diagnose a disease, and hold a conversation. |
| Other terms | Weak AI, Narrow AI | Strong AI, Artificial Superintelligence |
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve taken a comprehensive look at the fascinating world of Artificial Intelligence. We’ve explored the different types of AI – Narrow AI, General AI, and Artificial Superintelligence, each with its own unique capabilities and applications.
We’ve also discussed how AI learns and improves over time, much like us humans. Furthermore, we’ve touched upon the concept of AI autonomy and the Turing Test. Finally, we’ve distinguished between AI and AGI.
Understanding these concepts is crucial as AI continues to play an increasingly significant role in our lives.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into the diverse types of AI and their importance. Thank you for reading our valuable and informative stuffs.
FAQs Related to Types of AI
What’s Artificial Superintelligence?
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is a hypothetical future form of AI that surpasses human intelligence in all aspects, including learning, reasoning, creativity, and self-awareness. It’s not yet achieved and remains a topic of debate and exploration.
What Are 4 Types of AI?
The 4 types of AI are: 1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence, 2. Artificial General Intelligence, and 3. Artificial Superintelligence.
What Are The 3 Types of AI?
The 3 types of AI are: 1. Reactive Machines, 2. Limited Memory Machines, 3. Theory of Mind AI, and 4. Self-Aware AI
What Are The Different Types of AI?
The Different Types of AI are: Narrow AI, General AI, Super AI, Reactive Machines, Limited Memory Machines, Theory of Mind AI, and Self-Aware AI.