Have you ever pondered the history of Artificial Intelligence so fascinating! The concept of AI, machines mimicking human intelligence, was born in the mid-20th century.
Early pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy laid the groundwork, envisioning machines that could “think”. From simple rule-based systems in the 1950s to sophisticated neural networks in the 1980s, AI has evolved dramatically.
Today, AI is everywhere, from our smartphones to self-driving cars. Yet, this is just the beginning.
As we stand on the brink of further breakthroughs, the history of AI serves as a testament to human ingenuity and a glimpse into our future.
History of AI (Explained)
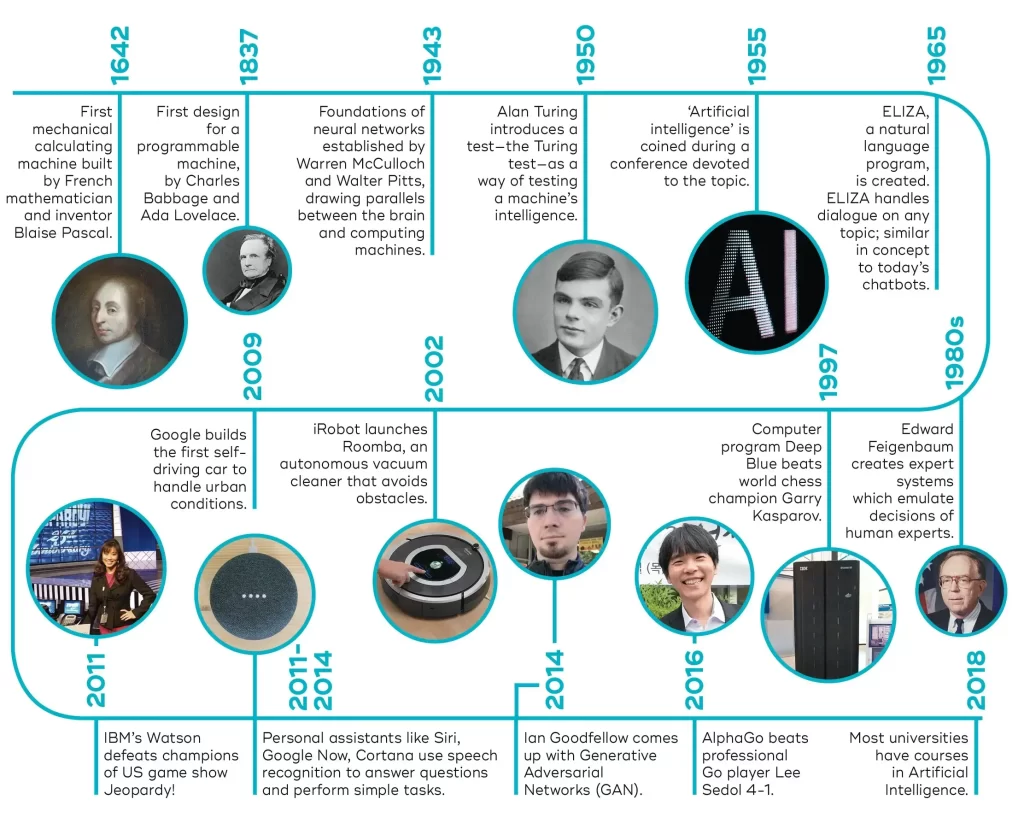
Seeds of Intelligence: The Dawn of AI (1940s – 1956)
This period witnessed the initial sparks of Artificial Intelligence, laying the groundwork for future advancements. While not yet formally named, research explored the possibility of building thinking machines.
Early Inspirations and Foundations (1940s)
- The Birth of Cybernetics: Norbert Wiener’s book “Cybernetics” (1948) explored the connection between machines and living systems, paving the way for thinking about information processing in both.
- Neural Network Beginnings: Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts proposed a model of artificial neurons in 1943, mimicking the basic structure of the brain and providing a foundation for future neural network research.
- Turing Test Introduced: Alan Turing published his seminal paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” in 1950, proposing a test to determine if a machine could exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from a human.
Pioneering Programs and Explorations (1950s)
- The First AI Program: In 1951, Christopher Strachey created a checkers program for the Ferranti Mark, considered the first AI program due to its strategic decision-making element.
- Logic Theorist Emerges: In 1955, Allen Newell, Herbert Simon, and Cliff Shaw developed the “Logic Theorist”, a program capable of proving mathematical theorems, demonstrating the potential of Artificial Intelligence for complex tasks.
- Perceptron’s Promise: Frank Rosenblatt built the Perceptron, a machine learning model inspired by the brain, capable of learning simple patterns, demonstrating the potential of machine learning for AI.
The Seeds of a Discipline (1956
- Dartmouth Workshop (1956): John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon organized a summer workshop at Dartmouth College, officially coining the term “Artificial Intelligence”. This landmark event brought together leading researchers and ignited widespread interest in the field.
This period marks the early exploration of AI, laying the groundwork for future research and development. From philosophical discussions to initial programs, the seeds of the field were sown, setting the stage for the exciting journeys of AI in the years to come.
The Golden Age of AI (1956-1974)
The period between 1956 and 1974 witnessed a surge in enthusiasm and progress in Artificial Intelligence research, often referred to as the “Golden Age”. This era was marked by several key milestones and significant advancements, setting the stage for future developments in the field.
The Birth of AI (1956)
- Dartmouth Workshop (1956): John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon organized a summer workshop at Dartmouth College, officially coining the term “Artificial Intelligence”. This event brought together leading researchers and ignited a wave of interest in AI research.
- Early Programs: Programs like Newell and Simon’s “Logic Theorist” and Rosenblatt’s “Perceptron” demonstrated the potential of AI for tasks like theorem proving and pattern recognition.
Progress and Promise (1956-1960s)
- Symbolic Reasoning: Research focused on developing logic-based systems that could reason and solve problems by manipulating symbols, leading to programs like ELIZA, an early chatbot.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Efforts aimed at enabling machines to understand and respond to human language, with projects like SHRDLU, a program that could understand questions and commands about a block world.
- Robotics: Development of early robots like Shakey, capable of navigating its environment and manipulating objects, sparked excitement about intelligent machines.
- Machine Learning: Early exploration of machine learning algorithms, with ideas like Rosenblatt’s perceptrons and Samuel’s checkers program paving the way for future advancements.
Challenges and Reassessment (1970s)
- Limitations of symbolic reasoning: As researchers encountered complex problems, the limitations of rigid symbolic systems became apparent.
- Funding cuts: Government funding for Artificial Intelligence research declined due to unfulfilled expectations of rapid progress, leading to a “winter” for AI research.
- New directions: Emergence of alternative approaches like knowledge representation and expert systems, laying the groundwork for future developments.
✅ How AI is Transforming The Dynamic World ✅
The First AI Winter: (1974 – 1980s)
Following the initial excitement of the “Golden Age”, the period between 1974 and the 1980s witnessed a significant setback for AI research, known as the “First AI Winter”. This era was characterized by decreased funding, skepticism, and limited progress.
Decline and Disillusionment (1974-1980)
- Unfulfilled promises: Overly optimistic predictions about Artificial Intelligence capabilities in the early years led to public disappointment when expected advancements failed to materialize.
- Funding cuts: Lack of significant breakthroughs caused government funding for AI research to plummet, hindering further development.
- Theoretical limitations: Researchers encountered the inherent complexity of problems like natural language processing and robotics, revealing the limitations of existing approaches.
- Perceptron controversy: Marvin Minsky’s influential book “Perceptrons” highlighted the limitations of early neural networks, discouraging research in that direction for a while.
A Glimmer of Hope (1980s)
- Expert systems: Emergence of expert systems, knowledge-based systems designed to capture and emulate human expertise, offered practical applications in specific domains.
- Lisp: The popularity of the Lisp programming language, well-suited for symbolic reasoning tasks, provided a valuable tool for Artificial Intelligence development.
- Knowledge representation: Research shifted towards representing knowledge in more comprehensive and structured ways, laying the groundwork for future advancements.
- Machine learning revival: Despite the setback, some researchers continued exploring machine learning, leading to developments like the backpropagation algorithm for neural networks.
The AI Renaissance (1980s – 2000s)
After the challenges of the first AI Winter, the period between the 1980s and the 2000s witnessed a significant revival of interest and progress in AI, often referred to as the “AI Renaissance”. This era was marked by several key developments and breakthroughs that laid the groundwork for the current state of Artificial Intelligence.
Expert Systems Take Center Stage (1980s)
- Boom of Rule-Based Systems: Expert systems, designed to capture and apply human expertise in specific domains, gained widespread adoption in areas like finance, medicine, and manufacturing.
- Lisp Dominates: Lisp programming language, well-suited for symbolic reasoning, becomes the lingua franca of AI development.
- Fifth Generation Project: Japan launches an ambitious initiative to develop advanced AI systems, further stimulating global research.
The Rise of Machine Learning (1990s)
- Machine Learning Revival: Advances in algorithms like backpropagation and support vector machines revitalize machine learning research.
- Statistical Learning Revolution: Focus shifts from symbolic reasoning to statistical approaches, leading to significant progress in tasks like image recognition and text analysis.
- Deep Blue Beats Kasparov (1997): IBM’s Deep Blue defeats chess champion Garry Kasparov, showcasing the potential of machine learning for complex tasks.
The Dawn of the Internet Age (2000s)
- Rise of Big Data: Explosion of digital data fuels the development of data-driven Artificial Intelligence models.
- Web Search Revolution: Emergence of search engines like Google, powered by advanced AI algorithms for ranking and understanding web content.
- Human-Computer Interaction Advances: Speech recognition and natural language processing technologies improve, paving the way for more natural interactions with machines.
The Age of Deep Learning: 2010s – Present
The period starting from the 2010s and continuing to the present day has been marked by the dominance of deep learning. This era has witnessed remarkable advancements in AI capabilities, leading to its widespread adoption across various sectors.
Deep Learning Explosion (2010s)
- Breakthroughs in Neural Networks: Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) achieve record-breaking performance in image recognition, leading to applications in self-driving cars, facial recognition, and medical diagnosis.
- Rise of Big Data and Computing Power: Increased availability of massive datasets and powerful computing resources like GPUs further fuel the development of deep learning models.
- Natural Language Processing Advancements: Deep learning revolutionizes NLP, enabling tasks like machine translation, chatbots, and sentiment analysis to reach new levels of accuracy.
AI Everywhere (2010s – Present)
- Democratization of AI: Cloud-based Artificial Intelligence platforms and tools make AI technology accessible to businesses and individuals, leading to widespread adoption in diverse domains.
- Impact on Industries: AI applications transform industries like healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and retail, automating tasks, optimizing processes, and generating insights.
- Emergence of AI assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant become ubiquitous, interacting with users and completing tasks using natural language processing.
The Present and Beyond
- Continued Progress: Ongoing research in areas like Explainable AI, Generative AI, and Reinforcement Learning pushes the boundaries of what AI can achieve.
- Ethical Considerations: Concerns about bias, fairness, and the potential societal impact of AI lead to calls for responsible development and deployment.
- Future Uncertainties: Questions about the long-term implications of advanced AI on jobs, inequality, and human control remain open for debate and discussion.
The Advancement of AI: Beyond 2024
While predicting the future with absolute certainty is impossible, considering trends and ongoing research paints a picture of what Artificial Intelligence might hold beyond 2024. Here are some potential areas of focus and development:
Democratization and Personalization
- AI as a tool: User-friendly tools and platforms will make AI accessible to individuals and small businesses, empowering them to solve problems and automate tasks.
- Personalized AI: AI will adapt to individual needs and preferences, offering personalized experiences in areas like healthcare, education, and entertainment.
Deeper Integration With Everyday Life
- Ubiquitous AI: AI will seamlessly integrate into various aspects of daily life, from smart homes and wearables to intelligent transportation and automated customer service.
- Enhanced decision-making: AI will assist individuals and organizations in making informed decisions by analyzing data, identifying patterns, and suggesting optimal courses of action.
Advances in Specific Areas
- Explainable AI: Efforts to make AI models more transparent and understandable will build trust and enable better human-AI collaboration.
- Generative AI: Progress in generating realistic text, images, and other creative content could lead to personalized experiences and advancements in fields like design and entertainment.
- Reinforcement Learning: Artificial Intelligence agents learning through trial and error could excel in complex environments, potentially leading to breakthroughs in robotics and autonomous systems.
Continued Challenges and Considerations
- Ethical considerations: Addressing bias, fairness, and potential job displacement will remain crucial concerns, requiring continuous ethical evaluation and responsible development.
- Regulation and governance: Establishing clear guidelines and regulations will be essential to ensure safe and beneficial use of AI.
- Human-AI collaboration: The focus will shift towards effective collaboration between humans and AI, leveraging their complementary strengths to solve complex problems.
Beyond 2024
- Superintelligence: While still a distant possibility, discussions about hypothetical super intelligent AI and its potential impact will continue.
- New frontiers: Research in areas like quantum computing and neuromorphic computing could lead to further breakthroughs and redefine the future of Artificial Intelligence.
Conclusion
Finally, we’ve taken a fascinating tour through the history of artificial intelligence, from its humble beginnings in the 1940s to now and beyond.
We’ve experienced the golden age, the AI winters, and the rise of deep learning. As we look ahead, we see boundless possibilities for AI advancement after 2024.
This investigation has given us not only an improved understanding of AI’s past but also a glimpse into its future.
We hope that this article has answered your queries and sparked your interest in the constantly developing topic of artificial intelligence.
Thank you for joining us on this historical voyage through artificial intelligence.
FAQs Related to History of Artificial Intelligence
What Was the Beginning of AI?
The beginnings of AI are murky, with roots in ancient philosophy and mathematics. However, the modern field arguably started in the 1950s with pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy laying the groundwork.
Who Invented the First AI?
The First AI was carried out by British logician and computer pioneer Alan Turing. Ross Quillian, on the other hand, used a semantic network to develop the first AI program.
Who is the Father of AI?
John McCarthy is regarded as the “father of AI” by many because of his contributions to the 1950s AI idea development.
When Was AI Invented?
The idea of “artificial intelligence” (AI) was first used between 1950 and 1956. The Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence formally established the field of AI in 1956.
